Angular custom validation using AsyncValidator with Observable
Aug 6, 2017 • 5 minute read
Summary
- Based on Angular v4.3.
- Quick look at Angular reactive forms and validators.
- Setting up custom async validation (AsyncValidator) using an Observable with a service.
The example we’ll build
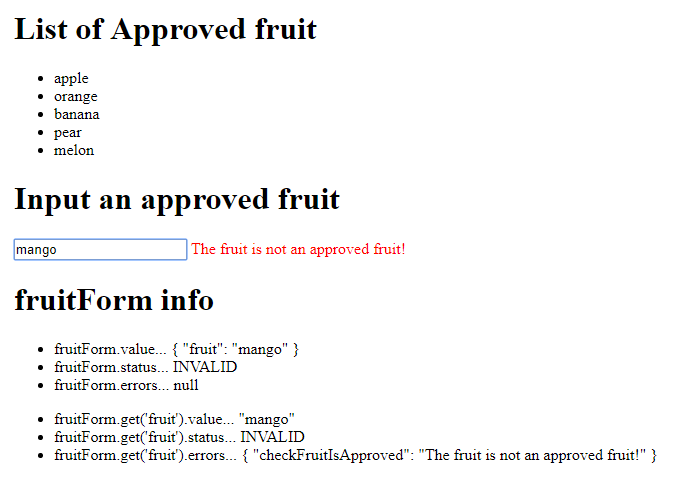
Things to mention
- The angular
ReactiveFormsModulewill need to be added to our moduleimports. - We’ll also need to add our
FruitServiceto the moduleproviders.
Building the reactive form
Angular’s FormBuilder class can be used to construct new FormGroup, FormControl and FormArray objects that can be used to build an Angular reactive form.
- Declare a local
FormGroupvariable so we can reference our form. - Inject
FormBuilderinto our component class. - Use the
FormBuilder.groupmethod to build our reactive form by passing in details of whatFormControlobjects should be added to theFormGroup.
FormBuilder.group(
controlsConfig: {[key: string]: any},
extra: {[key: string]: any}|null): FormGroup
- The first parameter for
FormBuilder.grouptakes an object of key-value pairs.- The key is what we’ll use to reference the
FormControl. - The value is the initialisation info for the
FormControlobject to be created. We’ll pass an array.- First item is the initial value.
- Second item is an array of sync validators.
- Third item is an array of async validators.
- The key is what we’ll use to reference the
- The second parameter is an object to specify sync validators and async validators to be applied at the
FormGrouplevel. - We’re passing in our validators at
FormControllevel instead.
Excerpt from app.component.ts
public fruitForm: FormGroup;
public constructor(
private formBuilder: FormBuilder,
private fruitService: FruitService
) {
this.fruitForm = formBuilder.group({
fruit: [
'',
[Validators.required ,Validators.minLength(4)],
[(control: AbstractControl): Observable<ValidationErrors | null> =>
this.checkFruitIsApproved$(control)]
]
})
}
- We are using an arrow function to provide our
AsyncValidator, so that the value ofthiswithin ourcheckFruitIsApproved$function is appropriately scoped.
Performing validation
Angular will always process the sync validators first. Only when all of the sync validators pass will angular then process any async validators.
- Our AsyncValidator
checkFruitIsApproved$receives anAbstractControlobject which is what is being validated. - We need to return an
Observable<ValidationErrors | null>. - We pass the value of our control to a service to process validation.
Excerpt from app.component.ts
public checkFruitIsApproved$(control: AbstractControl): Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return this.fruitService.fruitIsApproved$(control.value)
/// CODE OMITTED //
}
Excerpt from fruit.service.ts
@Injectable()
export class FruitService {
public fruitIsApproved$(fruit: string): Observable<boolean> {
let approvedFruit: Array<string> = ['apple', 'orange', 'banana', 'pear', 'melon'];
let isApproved: boolean = approvedFruit.includes(fruit);
return Observable.of(isApproved)
.delay(1000);
}
}
- Our mock service returns an
Observable<boolean>to indicate validation pass or fail, building in a delay of 1000ms to simulate what would normally be a HTTP GET.
Excerpt from app.component.ts
public checkFruitIsApproved$(control: AbstractControl): Observable<ValidationErrors | null> {
return this.fruitService.fruitIsApproved$(control.value)
.map(response => {
if (response) {
return null;
} else {
return {checkFruitIsApproved: 'The fruit is not an approved fruit!'};
}
});
}
- We call
.mapon our Observable so we can manipulate the stream. - If the response is false, the validation has passed and we return null.
- Otherwise the validation has failed and we return an object with a key-value pair.
- The key is what we will use to reference the error, the value we will set to our error message.
Our html
- We add
[formGroup]="fruitForm"to bind ourfruitFormFormGroupto the form. - We add
novalidateto stop any built in validation that we’re not in control of. - We add
[formControlName]="'fruit'"to bind ourfruitFormControlto the input element. - The first span element will show if our
'checkFruitIsApproved'error is present on thefruitFormControl. The inner text of the span will display the error message we set as the value for the error key. - The second span element will show if the
fruitFormFormGroupis valid.
<form [formGroup]="fruitForm" novalidate>
<input [formControlName]="'fruit'">
<span *ngIf="fruitForm.controls['fruit'].hasError('checkFruitIsApproved')" style="color: red;">
</span>
<span *ngIf="fruitForm.valid" style="color: green;">
Outstanding, that fruit is approved!
</span>
</form>
Wrap up
- Angular will only process AyncValidators if all (sync) Validators in the
FormGrouphave passed (sync) validation. - Validators can be applied at
FormGrouporFormControllevel. - If a
FormControlis invalid, its parentFormGroupwill also become invalid, however, the error information (key-value pair) will not rollup toFormGrouplevel.
Contact me
Email me at chum@chumtoadafuq.email.
